Harry S. Truman was the first of 3 kids created to John Anderson Truman, a farmer and mule trader, and the wife of his, Martha Ellen Truman. Although the parents of his could not decide on a middle name, Harry was named in honor of the maternal uncle of his, Harrison Young. After over a month, they settled on merely utilizing the letter S as a tribute to both the maternal grandfather of his, Solomon Young, and the paternal grandfather of his, Anderson Shipp Truman.
Truman were raised on the family farm in Independence, Missouri, and didn’t attend college. He worked a number of jobs after high school, initially as a timekeeper for a railroad building business, and then as a bookkeeper and a clerk at 2 individual banks in Kansas City. After 5 yrs, he returned to farming and joined the National Guard.
When World War I erupted, Truman volunteered for duty. Though he was thirty three years old – 2 years older compared to the age cap for the draft – as well as qualified for exemption as being a farmer, he helped manage his National Guard regiment, that had been eventually called into service in the 129th Field Artillery. Truman was promoted to captain in France and assigned Battery D, that had been known to be most unruly battery in the regiment. In spite of a modest and shy temperament, the respect was captured by Truman and admiration of the men of his and led them successfully through heavy combat during the Meuse Argonne campaign.
After the battle, home was returned by Truman and married the childhood sweetheart of his, Elizabeth Bess Wallace in 1919, with who one daughter was had by him, Mary Margaret. That very same year, he launched a foray into business as he and an associate, Eddie Jacobson, create a hat store in Kansas City. But with America encountering an economic decline in the early 1920s, the company failed in 1922. With all the closing of the company, Truman owed $20,000 to creditors. He refused to recognize bankruptcy and insisted on paying back again all of the cash which took over fifteen years.
Truman was elected to the United States Senate in 1934. In the first term of his, he served on the Senate Appropriations Committee, which was liable for allocating tax money for Franklin Delano Roosevelt’s New Deal tasks, and the Interstate Commerce Committee, which oversaw interstate, shipping, and railroads transport. Along with Senator Burton Wheeler, Truman began investigating railroads, and in 1940, he initiated legislation that enforced tighter federal regulation on the railroads, that aided him build the reputation of his as a man of integrity.
By the time Truman was in place for reelection in 1940, Thomas Pendergast was convicted of tax evasion and connected with voter fraud, along with many expected Truman’s link with Pendergast would lead to a defeat. Truman did not attempt to hide or perhaps distort the relationship of his with Pendergast, Nonetheless, and the reputation of his as an ethical and frank man helped him win reelection, albeit narrowly.
In the second term of his, Truman chaired a specific committee to explore the National Defense Program to stop war profiteering and careless spending in defense industries. He received public recognition and support for his simple stories and pragmatic tips, as well as he received the admiration of the colleagues of his as well as the populace alike.
When FDR had to pick a running mate for the 1944 presidential election, the acting vice president of his, Henry Wallace, was deemed unacceptable. Wallace was disliked by many of the senior democrats in Washington, and since it was obvious that Roosevelt may not survive the fourth term, the vice presidential choice was particularly crucial. Truman’s popularity, in addition to the reputation of his as a fiscally responsible male along with a defender of citizens’ rights, made him an appealing choice. Although after the nomination was received by him, he campaigned vigorously, Truman was at first reluctant to accept.
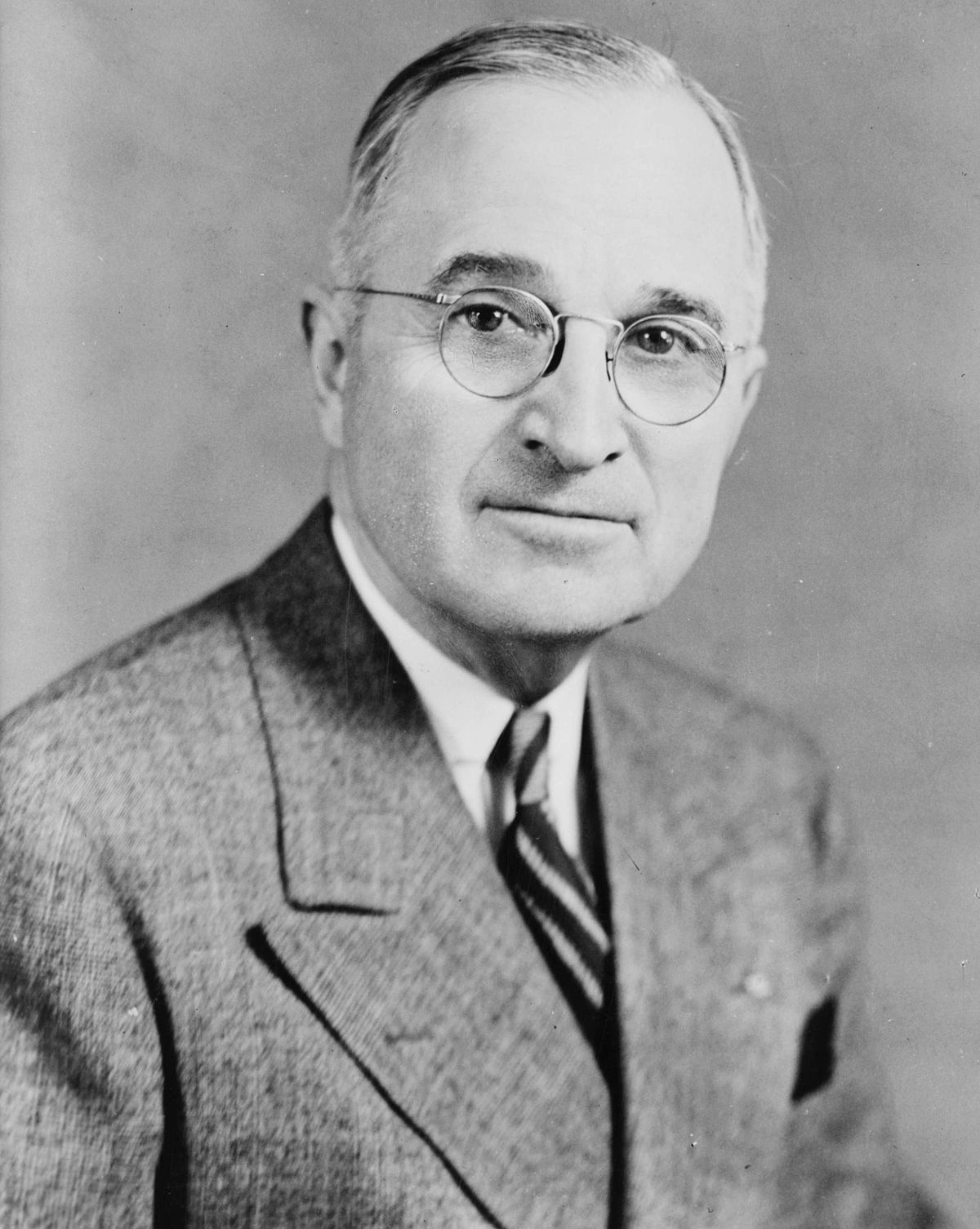
Truman and Roosevelt had been elected in November of 1944, and Truman had taken the oath of on January twenty, 1945. He served as vice president only eighty two days before Roosevelt died associated with a massive stroke and thus he was sworn in as president on April twelve, 1945.
With no previous experience in policy that is foreign, Truman was thrust into the job of commander in chief and charged with ending a world war. In the first 6 months of the term of his, he announced the Germans’ surrender, dropped atomic bombs on Nagasaki and Hiroshima – ending World War II – and also signed the charter ratifying the United Nations.
After the War In spite of these first successes, Truman’s diplomatic scenario was beset with obstacles. Although the Soviet Union were definitely a strong friend to the United States during the battle, international associations deteriorated fast when it started to be apparent that the Soviets intended to stay in control of Eastern European nations that have been expected to be reestablished based on their pre- Hitler governments. This, together with the exclusion of the Soviets from the reconstruction of Asia, started the Cold War.
Republicans dominated both houses of Congress in 1946, that had been viewed as a judgment of Truman’s policies, and polls suggested that reelection was all but impossible. So certain looked the victory of New York Governor Thomas Dewey which the Chicago Tribune famously went to press with the title “Dewey Defeats Truman” before many polling places had released outcomes. The final effect was a win for Truman with 49.5 % of the vote, compared with Dewey’s 45.1 %, and it was among the biggest upsets in the story of American elections.
Truman announced the domestic policy initiative of his, the Fair Deal program, in his 1949 State of the Union address. Building on Roosevelt’s New Deal, it provided universal health care, a rise in the minimum wage, much more funding for education along with a promise of equal rights under the law for most citizens.
The system was a mixed success. In 1948, racial discrimination was banned in federal government hiring practices, the army was desegregated as well as the minimum wage gone up. National health insurance was rejected, as was even more money for training.
The Korean War broke out in June of 1950, and Truman quickly committed U.S. troops on the struggle. He thought that North Korea’s intrusion of South Korea was challenging out of the Soviets, which, if still left unchecked, could escalate to another world war as well as to even more communist aggression. After a brief trend of public support for the decision of his, criticism mounted.
Truman originally endorsed a rollback approach and then encouraged General Douglas MacArthur to breach the 38th parallel, taking forces into North Korea to dominate the government. But when China delivered 300,000 troops to the aid of North Korea, tactics were changed by Truman. He reverted to the containment tactic, focusing on protecting the independence of South Korea instead of eliminating communism in the north. MacArthur publicly disagreed. To Truman, that was insubordination and challenging to the authority of his, as well as he dismissed MacArthur in April of 1951. MacArthur was obviously a popular general, as well as Truman’s already weak approval rating declined even further.
In March of 1952, Truman announced that he wouldn’t run for reelection. He gave the support of his to Governor Adlai Stevenson, the democratic nominee, although Stevenson was distancing himself from the president due to his bad approval rating.
After retiring from the presidency, Truman returned to Independence, Missouri, wherever the memoirs of his were written by him, oversaw the building of the presidential library of his and also took long walks. He died on December twenty six, 1972, and it is installed alongside Bess in the courtyard of the Truman Library.












Add Comment